
A 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve is a device that controls fluid flow through two ports. The term ‘2/2 Way’ signifies two ports and two operational states: open and closed. This 2/2 way solenoid valve operates by using a direct acting solenoid valve, which utilizes an electromagnetic solenoid to either allow or block the passage of fluids. This mechanism is crucial in various applications, including high pressure solenoid valve systems and stainless steel valves, ensuring durability and reliability. Additionally, understanding the working principle solenoid valve is essential for effective implementation in pneumatic systems.
Key Takeaways
- A 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve controls fluid flow through two ports, operating in either an open or closed state.
- Understanding the difference between Normally Closed and Normally Open valves helps in selecting the right type for safety and efficiency.
- Regular maintenance of valve components is crucial to prevent failures and ensure optimal performance in various applications.
Operational Mechanics of 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve

Role of the Solenoid
The solenoid plays a pivotal role in the operation of a 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve. It acts as the driving force that converts electrical energy into mechanical movement. When electrical current flows through the solenoid coil, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field attracts or repels a ferromagnetic plunger, which subsequently opens or closes the valve port.
The solenoid coil generates a magnetic field when electrical current flows through it, which attracts or repels a ferromagnetic plunger. This movement either opens or closes the valve port, effectively regulating fluid flow.
This electromechanical conversion is fundamental to many real-world applications, including solenoid valves, where the plunger’s movement directly controls the flow of liquids or gases. The efficiency of this process significantly impacts the overall performance of the valve, making the solenoid a critical component in various systems.
Components of the Valve
Understanding the components of a 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve is essential for grasping its operational mechanics. Each part serves a specific function that contributes to the valve’s overall performance. The table below outlines the key components and their respective functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Solenoid Coil | Converts electrical energy into mechanical motion to open or close the valve. |
| Plunger or Armature | Moves to open or close the valve’s orifice based on the magnetic field from the coil. |
| Valve Body and Ports | Houses internal components and provides pathways for fluid or gas with an inlet and outlet. |
| Orifice | The opening that allows fluid or gas to flow; its size affects flow rate. |
| Seal or Diaphragm | Prevents leaks when the valve is closed, ensuring complete flow stoppage. |
| Return Spring | Returns the plunger to its original position, maintaining the valve’s default state. |
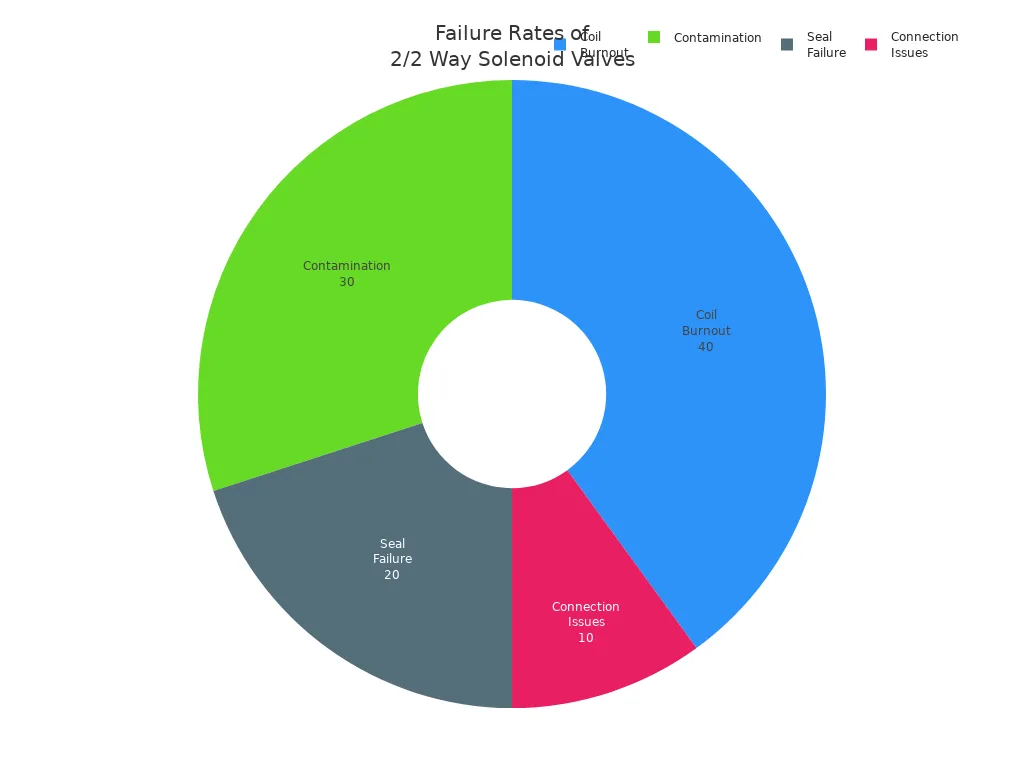
Each component works in harmony to ensure that the 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve operates efficiently. Regular maintenance of these components is crucial to prevent common failure modes, such as coil burnout or seal failure, which can lead to operational issues.
Types of 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves
Normally Closed
Normally Closed (NC) 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves remain in a closed position when not energized. This design prevents fluid flow until the solenoid is activated. The default closed state is crucial for applications requiring safety and reliability.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Default Position | Closed (no compressed air can flow through) |
| Energized Position | Open (allows air to flow when the solenoid is energized) |
| Ports | Two ports: an inlet/supply port and an outlet/exhaust port |
| Function | Controls on-off flow of compressed air |
| Essential Use | Starting or stopping the flow of gaseous media |
In many scenarios, NC valves are preferred due to their safety features. For instance, in fluid control systems, they ensure that flow stops during power failures, preventing leaks and spills. Similarly, in pneumatic systems, these valves control the flow of compressed air to actuators, halting flow when power is lost. This characteristic makes them essential in hazardous applications, where stopping flow during power outages is critical to avoid environmental damage or system failures.
Normally Open
Conversely, Normally Open (NO) 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves allow fluid flow when de-energized. They close when the solenoid is activated. This configuration is suitable for applications where continuous flow is necessary until a specific action occurs.
- Normally open valves consume energy to remain closed, leading to higher energy usage in scenarios where they need to block flow.
- In contrast, normally closed valves consume energy only when activated to open, making them more energy-efficient in applications where they are closed most of the time.
The choice between NC and NO configurations should prioritize safety and energy efficiency. For example, in applications requiring constant flow, NO valves are ideal. However, for systems needing to stop flow during power loss, NC valves are the better option.
| Type | Description | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Normally Closed | Off without power, allows flow when energized. | Commonly used in applications requiring a default closed state. |
| Normally Open | On without power, allows flow when de-energized. | Suitable for applications needing a default open state. |
Understanding the differences between these two types of 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves is essential for selecting the right valve for specific applications. Each type serves distinct purposes and offers unique advantages based on operational requirements.
Applications of 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves

Industrial Uses
2/2 Way Solenoid Valves find extensive applications in various industrial processes. They play a crucial role in:
- Chemical processing
- Food and beverage production
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Water treatment
- Pneumatics
- Medical devices
- Manufacturing
These valves control chemical flows in processing plants and regulate water flow in treatment facilities. They also manage water flow in irrigation systems, ensuring efficient operation across diverse applications. Compliance with safety standards, such as UL, CSA, and CE, is essential for these valves in industrial settings.
Residential Applications
In residential settings, 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves control water flow effectively. They serve primarily for on/off applications, allowing homeowners to manage water resources efficiently. These valves connect to various fixtures and appliances, ensuring reliable operation. However, improper installation can lead to issues. For instance, incorrect orientation may prevent proper operation, and media pressure must remain within the valve’s operating limits.
Automotive Applications
In the automotive industry, 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves are vital for managing fuel and emissions. They ensure the efficient operation of various fluid circuits, contributing to overall vehicle performance. These valves help regulate fuel flow, enhancing engine efficiency and reducing emissions.
As industries evolve, the demand for 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves continues to grow, driven by technological advancements and a focus on sustainability.
In summary, 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves play a crucial role in various applications, from industrial processes to residential systems. Their design, including Normally Closed and Normally Open configurations, allows for precise control of fluid flow.
Understanding these valves is essential for engineers and technicians. They ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability across multiple sectors, including medical equipment and HVAC systems.
Key benefits include:
- Reduced water waste through accurate control.
- Increased agricultural efficiency via automation.
- Significant ROI, averaging around 3800%.
By grasping the mechanics and applications of 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves, professionals can optimize system performance and enhance operational efficiency.
FAQ
What is the primary function of a 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve?
A 2/2 Way Solenoid Valve controls fluid flow by opening or closing its ports based on electrical signals.
How do I choose between Normally Closed and Normally Open valves?
Select Normally Closed valves for safety applications and Normally Open valves for continuous flow needs.
What maintenance do 2/2 Way Solenoid Valves require?
Regularly inspect components for wear, clean the valve body, and ensure proper electrical connections to maintain optimal performance.
