
Yes, High-Temperature Solenoid Valves are often the optimal choice for industrial heating systems operating under extreme heat and demanding precise, reliable fluid control. These tough environments require components that can withstand intense conditions. For instance, a robustForged Brass Body Solenoid Valve handles high pressures and temperatures well. When you need a Solenoid Valve for Boiler operations or a Solenoid Valve for Industrial Heater systems, durability is key. A Stainless Steel Plunger Solenoid Valve ensures long-lasting performance even with very hot fluids.
Key Takeaways
- High-temperature solenoid valves are best for industrial heating systems. They work well in extreme heat and need precise fluid control.
- These valves use special materials like stainless steel and PTFE seals. This helps them handle very hot fluids and harsh chemicals.
- High-temperature valves are used in many places. They control steam, hot oil, and gas burners.
- These valves make systems safer and last longer. They also save money over time because they are reliable and need less repair.
- High-temperature valves are not always needed. Standard valves work for lower heat. Other valve types might be better for specific needs.
Understanding High-Temperature Solenoid Valve Technology

Defining High-Temperature Operation in Industrial Settings
When we talk about “high-temperature” in industrial settings, we mean conditions that push standard equipment to its limits. These are environments where fluids like steam, hot oil, or combustion gases reach extreme heat. A typical high-temperature solenoid valve handles media temperatures around 150°C (302°F) with an ambient temperature of 40°C (104°F). However, the definition can vary. Look at this chart to see how different valve types handle the heat:
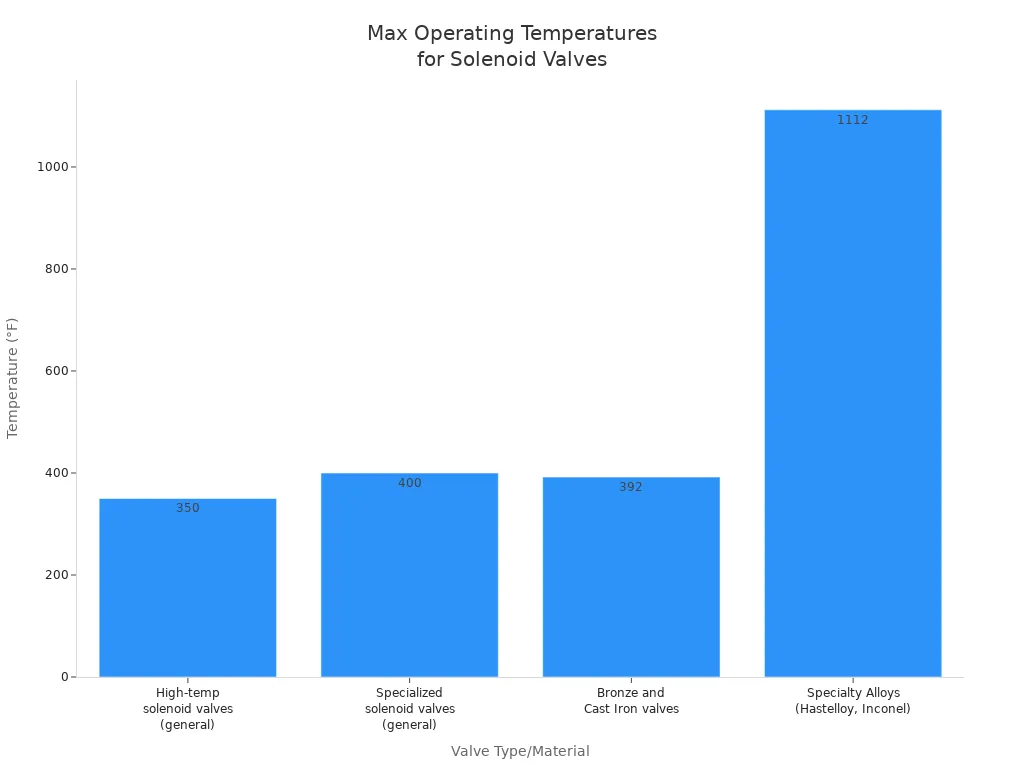
Industry standards also help define these conditions. For example, ASME B31.3 requires that the working temperature does not go over the material’s maximum limit. Other classifications, like Class PI, handle temperatures from 425 to 550℃, while Class PV deals with temperatures above 816℃, often needing special designs like heat insulation.
Key Design Features of High-Temperature Solenoid Valves
High-temperature solenoid valves are not just regular valves. They feature special designs to survive intense heat. Manufacturers choose specific materials for their bodies and internal parts.
- Body Materials:
- Stainless Steel: It offers great strength and resists corrosion, keeping things safe and reliable.
- Brass: This material resists corrosion and is easy to shape, working well across many temperatures.
- Sealing Mechanisms: Standard rubber seals quickly break down in high heat. High-temperature valves use special seals.
- PTFE (Teflon®): This polymer resists chemicals and extreme temperatures, making it perfect for seals.
- FKM (Viton®): This type of rubber works well with many chemicals and high temperatures.
- EPDM: This rubber resists water, steam, and high heat. These materials prevent leaks and ensure the valve works correctly.
- Coil Insulation: The coil, which creates the magnetic field, also needs protection. Coils are encapsulated to handle the heat and resist shock, moisture, oil, and chemicals.
- High-temperature coils often use Class H insulation. This allows them to operate in much hotter conditions than general service coils.
| Coil Class | Maximum Fluid Temperature | Maximum Ambient Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Class “B” | 212°F (100°C) | 104°F (40°C) |
| Class “H” | 400°F (206°C) | 212°F (100°C) |
These features ensure the valve performs reliably even when things get extremely hot.
Applications of High-Temperature Solenoid Valve in Industrial Heating

High-temperature solenoid valves play a vital role in many industrial heating systems. They precisely control the flow of hot fluids and gases, ensuring efficiency and safety. Let’s explore some key applications where these specialized valves truly shine.
Controlling Steam and Hot Water Systems with High-Temperature Solenoid Valve
Steam and hot water systems are common in many industries, from manufacturing to power generation. These systems rely on robust valves to manage extreme temperatures and pressures. For instance, a valve might need to handle 10 bar pressure at up to 185°C, or even 12 bar at 191.6°C.
| Pressure (bar) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| 10 | Up to 185 |
| 12 | 191.6 |
Choosing the right seals is also crucial. PTFE seals, for example, work well for steam-rated solenoid valves and high-temperature coils. They can withstand temperatures up to 200°C, which helps them last longer. While EPDM seals suit lower pressure steam up to 4.5 bar or 150°C, PTFE is generally a better choice for hot applications. This ensures a longer, trouble-free life for the valve.
These valves also handle various pressure applications:
- Low-pressure applications: Think about residential or small commercial heating systems, typically 15 to 50 psi.
- Medium-pressure applications: Industrial process heating or steam distribution systems often fall into this category, from 50 to 200 psi.
- High-pressure applications: Power generation or chemical processing plants might need valves for 200 psi or higher.
Valve design, materials like stainless steel or brass, and even the type of steam (saturated versus superheated) all affect how well a valve handles pressure.
Standard solenoid valves often face issues in steam applications, such as sticking or leakage. High-temperature designs address these problems. For example, they use Class H insulation for coils, which handles much higher temperatures than common Class F insulation. Installing heat sinks or insulation jackets also protects the coil and internal parts from direct heat. Industries like pharmaceuticals and food use steam for sterilization, needing valves that can withstand repeated heating and cooling without seal wear. Power plants also rely on these valves for high-pressure steam lines, demanding high thermal resistance and pressure durability.
Managing Hot Oils and Thermal Fluids with High-Temperature Solenoid Valve
Hot oils and thermal fluids are essential for heat transfer in many industrial processes. Controlling these fluids requires valves that can withstand their high temperatures and unique chemical properties. Material compatibility is a big concern here.
- Seals (gaskets, O-rings): These must match the specific fluid type and required temperatures. Quality and reputable sourcing are very important. Suppliers can help determine suitability.
- Metal components: Some metals can react with or be affected by the fluid. For instance, copper can act as an oxidation catalyst, and aluminum might experience pitting. Fluid providers are the best source for checking compatibility.
High-temperature solenoid valves prevent leakage and ensure safety in these demanding environments. They often use PTFE and red copper for effective sealing. All-metal sealing allows them to operate continuously with medium temperatures up to 350°C–450°C. An optimized sealing system ensures durability and higher efficiency for different media. These valves also feature a stainless steel piston structure with self-compensating valve core wear, which gives them a long service life. They can handle medium pressures up to 2.5–4.0 MPa, providing robust pressure handling and enhancing system safety.
Gas Combustion and Burner Control Using High-Temperature Solenoid Valve
Controlling gas flow to industrial burners is another critical application for high-temperature solenoid valves. These valves manage natural gas or propane, ensuring precise and safe combustion. They address several challenges in these systems. For example, they feature a ‘Class H (185°C)’ coil type and can operate in ambient temperatures up to ‘+115°C’. This ensures reliable performance in the high-temperature environments typical of industrial burners. They are also moisture resistant, which helps prevent operational issues and ensures longevity in potentially humid settings.
For high BTU applications, like those needing 10,000 up to 550,000 BTUs, these valves are specifically designed to handle significant gas flow and associated thermal loads. They often come with large port sizes, such as 1/8″ NPT and 1/4″ NPT Female, to manage gas flow efficiently.
Safety is paramount in gas combustion systems. Therefore, these valves must meet strict safety certifications:
| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| UL Certification | Shows compliance with safety standards for North America (United States and Canada). |
| CE Marking/ATEX Certification | Required for the European Union market, with ATEX specifically for safe operation in potentially explosive environments, including flammable gases and vapors. |
| CSA Certification | For valves designed for Canadian markets, also acceptable in some US hazardous applications. |
| IECEx Certification | An international certification for equipment used in explosive atmospheres, accepted globally for various hazardous applications. |
These certifications assure users that the valves meet rigorous safety and performance standards for hazardous gas applications.
Specialized High-Temperature Processes and Solenoid Valve Use
High-Temperature Solenoid Valve: 1
Benefits of High-Temperature Solenoid Valve for Your Heating Needs
High-temperature solenoid valves offer significant advantages for industrial heating systems. They provide robust performance and ensure smooth operations. These specialized valves bring many benefits, from lasting longer to making systems safer and more efficient.
Enhanced Reliability and Longevity of High-Temperature Solenoid Valve
These valves are built to last, even in the toughest heat. Their design focuses on durability, which means they work reliably for a long time. Manufacturers carefully choose materials for both the valve body and its sealing parts. This careful selection ensures the valve can handle extreme temperatures, resist chemicals, and stay strong mechanically. The right combination of materials helps the valve withstand stress and prevents leaks.
For example, the seals inside these valves are crucial. They use special materials that can handle intense heat and harsh chemicals.
| Seal Type | Features & Applications (High-Temperature Relevance) |
|---|---|
| FKM (Viton) | This material performs well in harsh chemical and high-temperature settings, including acids and solvents. |
| PTFE (Teflon) | This material is very inert and works across a wide temperature range. It suits highly aggressive fluids or media with suspended solids. |
These advanced seals prevent wear and tear, which often causes problems in standard valves. Many solenoid valves also include power reduction technology. This feature sends a full voltage pulse to activate the valve. Then, it reduces the current to a lower holding level. This process minimizes heat buildup in the coil, which greatly extends its service life. This is especially helpful in systems where valves operate frequently or for long periods. All these design choices mean fewer breakdowns and less need for replacements.
Improved Safety and Process Control with High-Temperature Solenoid Valve
Safety is a top priority in industrial heating, and these valves play a big role in keeping things safe. They work with automated control systems to prevent dangerous issues like gas leaks or system blowouts. You can program them to automatically shut off the flow of gas or refrigerant during emergencies. Most of these valves also have a fail-safe design. This means they automatically close if the power goes out or another emergency happens. This provides an essential layer of safety for your operations.
These valves are specifically engineered to work reliably in extreme thermal conditions where other valves would fail. Their advanced materials and features for managing heat extend their service life. They also reduce how often you need maintenance. This helps lower risks linked to managing high-temperature fluids. It ensures continuous operation, protects equipment from heat damage, and keeps productivity and safety high in industrial heating systems. High-temperature solenoid valves precisely control fluid or gas flow under extreme thermal conditions, often up to 300°C or higher. They use heat-resistant materials like stainless steel and PTFE seals. They also include design features such as heat-sink coils and specialized seals. This allows them to function reliably under thermal stress. This design prevents failures that could lead to hazards, ensuring safe, automated control in critical heat-exposed processes.
Long-Term Cost-Effectiveness of High-Temperature Solenoid Valve
While the initial cost of a high-temperature solenoid valve might seem higher, it offers significant savings over time. Their enhanced reliability means fewer unexpected breakdowns. This reduces costly downtime and lost production. You also spend less on maintenance and replacement parts because these valves last longer. The improved safety features prevent accidents, which can save companies from expensive repairs, legal issues, and potential harm to workers. By providing precise control, these valves also help optimize energy use in heating systems. This leads to lower energy bills. Investing in these durable and safe valves ultimately results in a better return on investment and lower overall operating costs for your heating needs.
When High-Temperature Solenoid Valve Might Not Be the Best Fit
Sometimes, a specialized valve is not always the best choice for every heating system. While high-temperature solenoid valves excel in extreme conditions, other options might suit specific needs better. Understanding these alternatives helps you make the right decision for your setup.
Considerations for Lower Temperature Applications
Not every industrial heating system operates under extreme heat. For applications with lower temperatures, standard valves often provide a more economical and practical solution. These systems do not experience the intense heat or pressure that demands the robust materials and design of a specialized valve. Using an oversized or over-engineered valve can lead to unnecessary costs without adding real benefit. Simple, general-purpose valves perform perfectly well in these less demanding environments. They offer sufficient control and reliability without the added expense of high-temperature capabilities.
Alternative Valve Types for Specific Industrial Heating Needs
Many other valve types exist, each with unique strengths for different industrial heating scenarios. For instance, ball valves offer a cost-effective option for stop valve applications, even at high temperatures. Metal-seated ball valves handle temperatures exceeding 750°F, reaching up to 1,500°F. Intermediate seat materials like R-PTFE (up to 450°F), PEEK (up to 550°F), and Carbon Fiber/Graphite-filled TFM (up to 580°F) bridge the gap between Teflon (400°F) and metal seats. Pressure seal valves also come in various sizes and pressure classes for high-temperature service.
Consider these alternatives for specific functions:
- Globe Valves: These valves offer superior throttling and stable flow characteristics. They are excellent for steam systems, power plants, and boiler feedwater control. They provide better shut-off than gate valves and are easy to repair.
- Gate Valves: They provide excellent sealing and low pressure drop when fully open. Power plants and water distribution systems often use them. However, they operate slowly and do not suit throttling.
- Pressure Relief Valves: These are crucial for safety in boilers and pressure vessels. They offer rapid response to overpressure, protecting equipment and personnel. They are economically viable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Choosing the right valve depends on your system’s specific requirements, including temperature, pressure, flow control needs, and budget.
High-temperature solenoid valves are a top choice for industrial heating systems. They give you robust, precise, and reliable fluid control, even in extreme heat. These valves handle tough conditions well. Always look at your specific operational parameters. This helps you decide if these specialized valves are the best solution for your heating needs.
FAQ
### What makes a solenoid valve “high-temperature”?
High-temperature solenoid valves use special materials. They feature stainless steel bodies and advanced seals like PTFE or FKM. These materials handle extreme heat and harsh chemicals. They also have special coil insulation, like Class H, to protect against high temperatures.
### Where do high-temperature solenoid valves get used?
Industries use them in many places. They control steam, hot water, and thermal fluids. You find them in gas combustion systems and industrial burners. They are also crucial for specialized processes needing precise fluid control in very hot environments.
### Are high-temperature solenoid valves always the best choice?
No, not always. They are best for extreme heat. For lower temperature applications, standard valves often work well and cost less. Other valve types, like ball valves or globe valves, might suit specific flow control needs better.
### How do high-temperature solenoid valves improve safety?
They enhance safety by working reliably in extreme heat. Their fail-safe designs automatically close during power outages or emergencies. This prevents leaks and system failures. They also meet strict safety certifications for hazardous gas applications.
