
For extreme environments, stainless solenoid valves often prove superior. They offer excellent performance where other materials fail. Brass solenoid valves for industrial use, however, show limitations in harsh conditions. When engineers consider brass vs stainless steel solenoid valves, they must evaluate several key factors. These factors determine the best material choice for demanding applications. Which material is better for solenoid valves? The answer depends on specific environmental challenges, making corrosion-resistant solenoid valves a critical consideration for any Solenoid Valve application.
Key Takeaways
- Stainless steel solenoid valves work best in harsh places. They resist corrosion, high heat, and strong pressure better than brass.
- Brass solenoid valves are cheaper at first. They work well for simple jobs with mild liquids and normal temperatures.
- Corrosive liquids and high temperatures can damage brass valves quickly. This makes them weak and causes leaks.
- Stainless steel valves cost more to buy. They save money over time because they last longer and need fewer repairs.
- Industries like food, medicine, and marine use stainless steel valves. These places need very strong and clean equipment.
Understanding Solenoid Valve Material Composition for Extreme Use
Choosing the right material for a Solenoid Valve is crucial, especially in tough conditions. The composition of the valve material directly impacts its performance and lifespan. Let’s look at what makes brass and stainless steel different.
Brass Solenoid Valve Alloys and Their Properties
Brass is a popular alloy for many valve applications. It mainly consists of copper and zinc. This mix gives brass a good balance of useful properties. It conducts heat well, machines easily, and resists wear. Different brass alloys exist, each with slightly varied compositions.
| Element | Composition Range |
|---|---|
| Copper | 55% to 90% |
| Zinc | 5% to 45% |
| Other elements (e.g., lead, nickel, manganese, tin) | Limited proportions |
These variations affect the brass’s strength and hardness. For example, Free Cutting Brass C36000 offers a tensile strength between 340-420 MPa. Naval Brass C46400 can reach 380-480 MPa. Hardness also varies among these alloys.
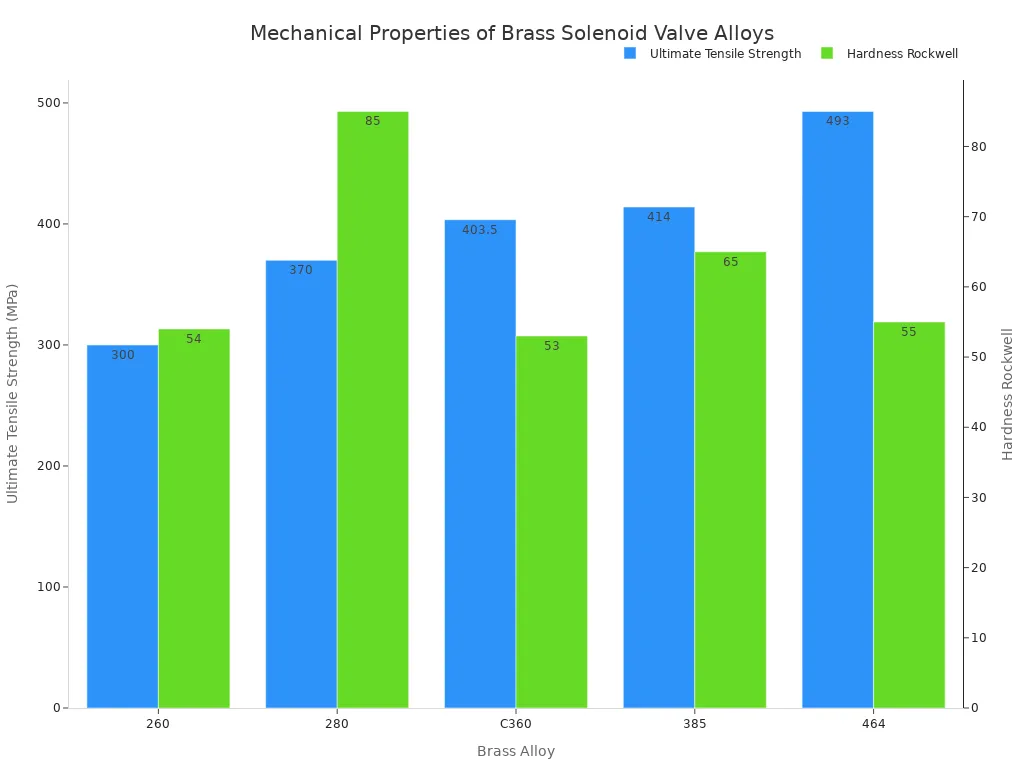
This chart shows how different brass alloys have varying ultimate tensile strength and Rockwell hardness. These mechanical properties are important for how the valve handles pressure and stress.
Stainless Steel Solenoid Valve Grades and Their Advantages
Stainless steel offers superior performance in extreme environments. Several grades are common for Solenoid Valves. Stainless steel 316 (1.4401) provides better resistance to corrosive conditions. This is because it contains molybdenum. Stainless steel 316L (1.4404) is similar to 316 but has less carbon. This makes it easier to weld and prevents corrosion at different temperatures. For high-temperature uses, stainless steel 316Ti (1.4571) includes titanium. This helps prevent corrosion after heating. A stronger option is stainless steel 1.4581, which adds nitrogen for increased strength.
When comparing stainless steel types, 316L often stands out against 304, especially in harsh settings.
| Feature | 304 Stainless Steel | 316L Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good for general use, not ideal for very corrosive environments (e.g., sea) | Better for corrosive environments, enhanced resistance to chemicals |
| Key Alloying Element | – | Contains molybdenum for extra resistance |
| Carbon Content | Standard | Lower carbon content |
| Welding & Temperature | – | Better for welding and varying temperatures without corrosion issues |
The molybdenum in 316L gives it extra protection against chemicals and saltwater. Its lower carbon content also makes it a better choice for welding without risking corrosion.
Corrosion Resistance of Solenoid Valves in Harsh Environments
Brass Solenoid Valve Vulnerability to Corrosive Media
Brass, a common material, struggles significantly in corrosive environments. It is generally not suitable for acids. When exposed to common industrial acids or bases, brass can degrade quickly. While specialized dezincification resistant brasses (DZR or DR), also known as corrosion-resistant brass (CR), exist for some situations, they are not universal solutions. Nickel-plated brass can handle weak organic or inorganic acids and alkalis. But, if the nickel layer gets compromised, corrosion will start.
Many corrosive media rapidly degrade brass components. Acidic environments cause quick degradation. Corrosive chemical media make brass valves lose integrity over time. Acidic fluid media and alkaline water accelerate dezincification. This process leaches zinc from the brass alloy. Aggressive chemicals and hard water also cause dezincification. This results in a porous structure, reduced strength, and potential leaks. Imagine a valve becoming weak and leaky; that is the risk with brass in these conditions.
Stainless Steel Solenoid Valve Superiority in Corrosive Applications
Stainless steel offers superior protection against corrosion. Its inherent properties, like the chromium oxide layer, resist many harsh chemicals. Grades like 316L, with their molybdenum content, provide even better resistance. This makes them ideal for demanding applications. SENYA’s high corrosion-resistant stainless steel valves are designed for such environments. They ensure consistency and stability, even when facing aggressive substances. This material choice means your systems run smoothly, without unexpected failures from corrosion.
Chemical Compatibility Challenges for Solenoid Valves
Choosing the right material means understanding chemical compatibility. Even stainless steel has its limits. Engineers must carefully match the valve material to the specific chemicals it will handle. Industry standards and certifications help confirm corrosion resistance. For example, IEC 60079 and ATEX directives provide guidelines for equipment in potentially explosive atmospheres. These often involve harsh chemicals. UL for safety standards and IEC for international electrical standards also ensure chemical resistance, adhesion strength, and durability under cyclic stress. These certifications are crucial for reliable performance. They give you confidence that your Solenoid Valve will perform as expected, even in the toughest chemical settings.
Temperature and Pressure Tolerance of Solenoid Valves

Valves must handle the heat and pressure of their environment. This is especially true for Solenoid Valves in tough settings. The material a valve is made from directly affects how well it performs under these conditions.
Brass Solenoid Valve Limitations at High Temperatures and Pressures
Brass valves face challenges when temperatures and pressures get too high. Brass has a lower melting point and cannot handle as much pressure as other materials. For example, standard brass valves with Viton® seals can typically handle up to 302°F and 225 PSIG. BUNA-N seals limit the temperature to 176°F.
| Seal Material | Max. Temperature | Max. Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Viton® | 302°F | up to 225 PSIG |
| BUNA-N | 176°F | up to 225 PSIG |
| EPDM | Not specified | up to 225 PSIG |
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause brass to deform. This leads to early valve failure. High-temperature fluids increase the risk of deformation and even rupture. The valve’s brass housing and seal materials must withstand the operating temperature to prevent them from breaking down. FKM and PTFE are better seal choices for high temperatures.
Stainless Steel Solenoid Valve Resilience in Extreme Conditions
Stainless steel valves show great strength in extreme heat and pressure. They handle tough conditions easily. For instance, a 316L stainless steel butterfly valve can operate up to 200°F and 110 PSIG. High-temperature stainless steel valves can work from -4 to 350°F. PTFE seals can even withstand temperatures from 32 to 356°F. Stainless steel, an alloy of iron with chromium and nickel, offers excellent resistance to corrosion, strength, and long-lasting durability. These features make it perfect for aggressive fluids, high heat, and high-pressure needs. SENYA’s robust stainless steel valves are known for their durability and performance. They resist wear and tear, ensuring a long service life in demanding places.
Thermal Cycling and Mechanical Stress on Solenoid Valves
Valves often experience thermal cycling, which means they heat up and cool down repeatedly. This can cause material fatigue, leading to tiny cracks and eventual failure. Rapid temperature changes create thermal shock, which also causes fatigue and potential structural problems. Extreme temperature swings put a lot of stress on materials, leading to failures and seal damage. For example, elastomer seals can become brittle and crack, causing leaks. Non-elastomer seals, like PTFE, handle temperature changes better. However, they still need careful design to prevent issues from expansion and contraction.
Durability and Longevity of Solenoid Valves
A valve’s ability to last a long time matters greatly. It needs to withstand constant use and harsh conditions. The material choice directly impacts how durable a valve is and how long it will serve.
Wear and Tear Resistance of Brass Solenoid Valves
Brass valves offer good durability in many standard applications. However, they face challenges in demanding environments. The plunger can experience high friction due to dirt, damage, or bending. Continuous cycling, exposure to varying pressures, and thermal expansion can cause moving parts like the plunger, spring, and diaphragm to weaken or break over time. Solenoid valves in high-frequency applications may wear out faster. Contamination and debris, such as dirt or rust particles, can accumulate inside the valve. This obstructs the movement of internal components, leading to performance degradation.
Stainless Steel Solenoid Valve Robustness and Service Life
Stainless steel stands out for its exceptional robustness and long service life. It possesses excellent structural strength. This enables it to endure extreme mechanical stress without compromising its integrity or operational capabilities. The inclusion of elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum further enhances its structural strength. This contributes to its overall robustness. This allows stainless steel valves to withstand repetitive mechanical stresses over extended operating periods. This holds true even in demanding environments like oil and gas production. SENYA’s high-quality stainless steel valves are built for this kind of resilience.
Impact of Abrasive Media on Solenoid Valves
Abrasive media, like sand or gritty fluids, can severely damage valves. These particles cause erosion and wear on internal components. Brass valves are more susceptible to this kind of damage. Their softer surface can quickly degrade when abrasive media passes through. Stainless steel, with its superior hardness and structural integrity, resists abrasive wear much better. This makes it a more reliable choice for applications involving abrasive fluids.
Cost-Effectiveness of Solenoid Valves for Long-Term Performance
When choosing valves, cost always plays a big role. People often look at the price tag first. However, true cost-effectiveness considers more than just the initial purchase. It includes how much money a valve saves or costs over its entire lifespan.
Initial Investment for Brass Solenoid Valves
Brass valves typically have a lower upfront cost. This makes them an attractive option for projects with tight budgets. Many businesses choose brass because it seems like a cheaper solution at first glance. For applications where conditions are mild and the valve does not face harsh elements, this initial saving can be a good deal. It allows companies to equip their systems without a large capital outlay.
Long-Term Value of Stainless Steel Solenoid Valves
Stainless steel valves, on the other hand, usually come with a higher initial price. This can make some buyers hesitate. However, their long-term value often outweighs this higher cost. Stainless steel offers superior durability and resistance to corrosion, extreme temperatures, and pressure. This means a stainless steel Solenoid Valve lasts much longer in demanding environments. It performs reliably for years, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This extended lifespan translates into significant savings over time.
Maintenance and Replacement Costs for Solenoid Valves
The real cost of a valve includes its maintenance and how often you replace it. Brass valves, especially in harsh conditions, may require more frequent maintenance or even full replacement. This adds up quickly. Think about the cost of new parts, labor for repairs, and potential downtime for your operations. Stainless steel valves, due to their robust nature, demand less maintenance. They also need replacement far less often. This reduces ongoing operational expenses and keeps systems running smoothly with fewer interruptions. Investing in stainless steel often means fewer headaches and lower total costs in the long run.
Application-Specific Suitability of Solenoid Valves
Choosing the right valve material is crucial for any system. Different applications have different needs. This section explores when to use brass and when stainless steel becomes essential.
When Brass Solenoid Valves are Acceptable
Brass valves work well in many situations. They are a good choice for non-aggressive fluids. These include regular water or non-acidic liquids. Brass also suits low to medium-pressure and temperature settings. Projects with tight budgets often choose brass. It costs less to buy and make compared to steel. HVAC systems can use brass when extreme cleanliness is not a top priority. Brass is inexpensive and easy to machine. This leads to lower production costs. It provides durable valves within its operational limits.
| Application/Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-aggressive fluid service | Suitable for pipelines handling regular water and non-acidic fluids. |
| Low to medium-pressure and temperature | Ideal for applications within these pressure and temperature ranges. |
| Cost-sensitive projects | Cheaper to acquire and produce compared to steel counterparts. |
| HVAC applications | Viable where extreme hygiene requirements are not necessary. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Brass is relatively inexpensive and easy to machine, leading to lower production costs and durable valves within allowable operational limits. |
Critical Applications Demanding Stainless Steel Solenoid Valves
Some applications absolutely require stainless steel. These are environments with corrosive chemicals or extreme temperatures. High-pressure systems also benefit from stainless steel’s strength. Marine and offshore settings need stainless steel because of saltwater. SENYA’s robust stainless steel valves excel in these demanding places. They offer reliability where other materials fail.
Solenoid Valves in Food, Pharmaceutical, and Chemical Processing
Food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries have strict requirements. They need materials that do not contaminate products. Stainless steel, especially grades like 316L, is ideal here. It resists corrosion from cleaning agents and process fluids. Its smooth surface also prevents bacterial growth. This ensures product purity and safety.
Solenoid Valves in Marine and Offshore Environments
Marine and offshore environments present some of the toughest challenges for industrial equipment. Solenoid valves in these settings face constant assault from harsh elements. High pressure, relentless corrosion from seawater, and even biofouling significantly impact valve performance and longevity. These conditions demand materials that can withstand extreme stress.
Consider the immense pressures involved. Some applications, especially in deep-sea drilling, face pressures exceeding 10,000 psi. This necessitates advanced materials and robust designs. These designs prevent leaks and ensure consistent operation. Corrosive seawater and various chemicals used in drilling operations rapidly degrade valve components. This requires specialized coatings and alloys. Stainless steel, particularly grades like 316L, offers superior resistance to these aggressive substances.
Maintaining valve integrity in these conditions requires robust designs. It also needs corrosion-resistant alloys. Sealing mechanisms must withstand pressure differentials. They also prevent water ingress. This requires high-quality seals and gaskets. Environmental factors like temperature fluctuations also play a role. From cold deep-sea waters to high temperatures from drilling, these changes affect material properties. They also impact fluid viscosity.
Remote locations and limited access for maintenance and repair demand highly reliable valve systems. These systems need extended service lives and minimal maintenance. The risk of seal degradation or valve malfunction is high. This can lead to leakage of hydraulic fluids or drilling muds. Such leaks harm marine ecosystems. Corrosion of metals in valve construction over time also releases harmful substances. Therefore, stainless steel valves are not just a choice; they are a necessity for safety and environmental protection in marine and offshore applications.
Installation and Maintenance of Solenoid Valves
Proper installation and regular maintenance are crucial for any valve system. The material of a valve significantly impacts these processes. Understanding these differences helps ensure long-term performance and reliability.
Ease of Installation for Different Solenoid Valve Materials
Installing stainless steel valves requires careful attention to detail. Installers should use anaerobic liquid pipe sealant for high-reliability connections. They must also ensure the valve ports remain plugged until connection to prevent contamination. Always install the valve according to the flow arrow on its body. Incorrect installation can cause continuous leakage. Mount the coil vertically to maximize armature lifespan. This prevents uneven wear. For high-temperature lines, avoid overtightening tapered threads on a hot stainless body. This prevents seat warping. Installers must also incorporate expansion loops in piping to prevent stress. They should never insulate the coil; it needs free air for heat dissipation. For pilot-operated valves, verify the minimum differential pressure. Install an upstream Y-strainer to prevent contamination.
Routine Maintenance Requirements for Solenoid Valves
All valves benefit from routine maintenance. Maintenance intervals can range from monthly to quarterly, depending on the application. Key activities include visual inspections for corrosion, leakage, or unusual wear. Functional testing verifies actuation timing and responsiveness. Technicians perform leak checks and cycle testing. Logging all maintenance activity helps identify patterns or recurring issues. Pre-scheduled replacement of seals or diaphragms, based on usage cycles, also extends valve life.
Repair and Replacement Frequency of Solenoid Valves
Several signs indicate a valve needs repair or replacement. The compressor might not unload after reaching pressure. The machine could continue to operate when it should shut off. Pressure might experience spikes or unstable regulation. The valve could become stuck open or closed. Sluggish startup or failure to load also signals a problem. Audible sounds like clicking, hissing, or irregular cycling are also indicators. Stainless steel valves are significantly more durable in harsh conditions. They withstand over 500,000 cycles under normal use. They also handle around 200,000 cycles in corrosive or high-temperature environments. Brass or plastic valves are prone to cracking or wearing out quickly with repeated thermal cycles. This means a much shorter lifespan and higher replacement frequency compared to stainless steel.
For extreme applications, stainless steel Solenoid Valve options clearly stand out. Engineers must always match the valve material to specific environmental demands. This ensures optimal performance and prevents costly failures. Stainless steel offers the definitive choice for reliable operation in harsh conditions. It provides superior durability, corrosion resistance, and long-term value, making it an indispensable component for critical systems.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of stainless steel solenoid valves for extreme use?
Stainless steel solenoid valves offer superior durability and corrosion resistance. They handle harsh chemicals, high temperatures, and extreme pressures much better than brass. This makes them ideal for demanding industrial environments.
Why do brass solenoid valves struggle in corrosive environments?
Brass contains copper and zinc. Corrosive media, like acids or saltwater, can cause dezincification. This process removes zinc, making the brass porous and weak. This leads to leaks and early valve failure.
Can brass solenoid valves handle high temperatures and pressures?
Brass valves have limitations at high temperatures and pressures. They can deform or fail under extreme conditions. Stainless steel maintains its integrity better, making it suitable for more demanding thermal and pressure applications.
Is the higher initial cost of stainless steel solenoid valves worth it?
Yes, the higher initial cost often provides long-term value. Stainless steel valves last longer and require less maintenance. This reduces replacement frequency and operational downtime, saving money over the valve’s lifespan.
Which industries commonly use stainless steel solenoid valves?
Many critical industries rely on stainless steel solenoid valves. These include food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. Marine and offshore environments also demand stainless steel for its robust performance against harsh elements.
